Ballistic Missile Defences (BMD)
Ballistic missile defence systems often work by using a kinetic kill vehicle to smash into its target.
Let’s consider an attacking country launching an Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile, or ICBM, against a defending country.
There are 4 different phases of a ballistic missile flight that we will consider: boost, post-boost, mid-course, and terminal.
The boost phase lasts between 3 and 5 minutes depending on whether the ICBM is solid, or liquid fuelled. This is technically the easiest time to shoot the missile down however this is usually impractical due to the location of the missile from interceptors at the time.
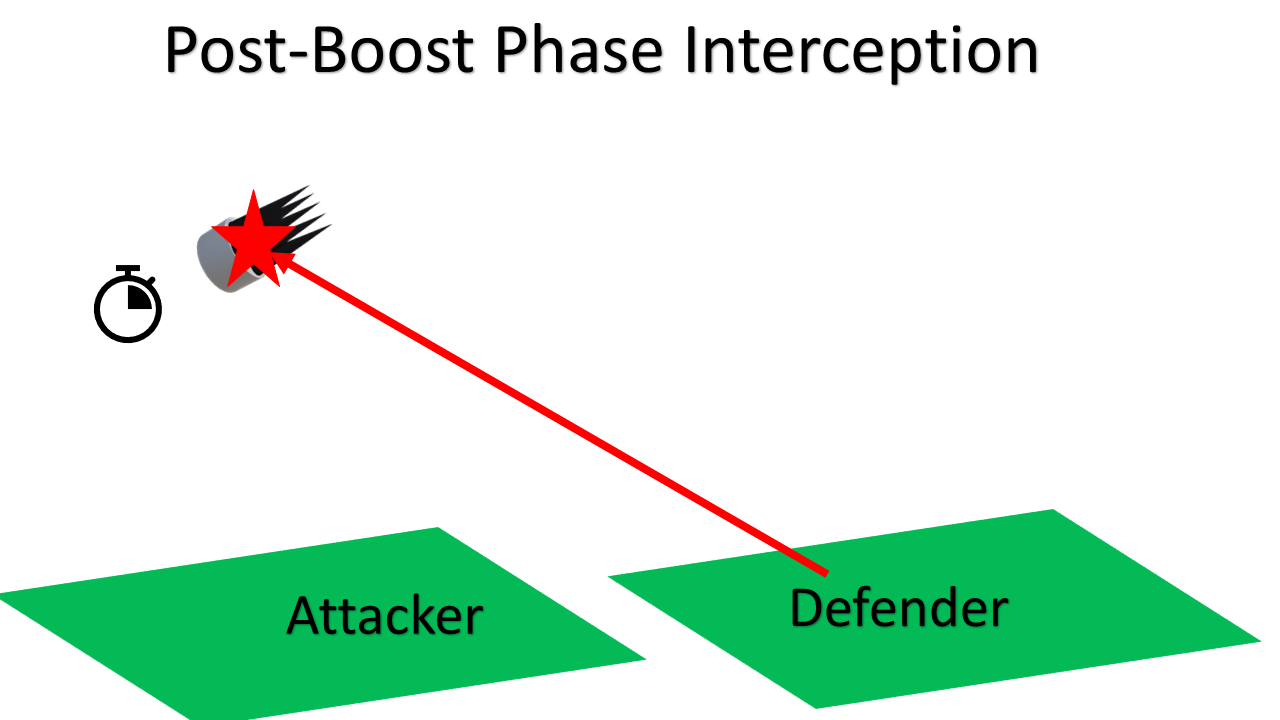
The post boost phase can last between 5 and 10 minutes where the post boost vehicle, or bus, manoeuvres into predesignated locations to release warheads and decoys. Intercepting the bus is more difficult than intercepting the entire missile, but far easier than intercepting each object released by the bus.
The midcourse phase can last 20 minutes, when the warheads and decoys travel through the vacuum of space. Without air resistance all objects released travel at the same speed irrespective of their size or mass.
Missile defence countermeasures include;
booster fragments of varying shapes and sizes,
metallic strips called chaff which reflect radar waves
creating radar clutter,
inflatable balloons, made of a radar reflective material,
carrying either a warhead or a small heater to give the balloons different
temperatures,
lightweight inflatable imitation warheads,
radar jammers,
and stealth coatings which reduce the warheads radar cross section and also its temperature to better blend in with the cold background of space.
In this phase it can be impossible to distinguish between real warheads and countermeasures so all objects must be intercepted, this can quickly exhaust the defenders’ interceptors.
The terminal phase may only last a minute, where lightweight decoys slow down and burn up and the heavy warheads re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere. There are less targets to intercept than in the midcourse phase, but terminal phase interceptors have limited range and must respond quickly.











Comments
Post a Comment